Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)
Flexible automation systems prolong the capacities of programmable systems to make it possible for transitions with minimal or no loss of manufacturing time. Adaptable liquid filling machine systems can deal with a variety of products in medium-sized quantities.
Programmable
Programmable automation systems permit adaptation and reordering of procedures to accommodate variants and customization of production. They usually consist of mathematical control machine tools that a computer system program goes to generate sets of various objects. Sets can consist of a couple of or several thousands of objects.
For better efficiency, programmable automation systems slate batches of comparable products for consecutive production. Programmable automation lines consist of non productive durations, throughout which the system adjusts over equipment and reprograms controls in between batches.
Inflexible, Hard, or Fixed
In fixed automation systems, the devices dictates the sequence of processes. These procedures either cannot be changed or can only be adjusted with great effort. The result is usually limited to one product made in high volumes, such as automobiles.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)/ Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
Computer-aided design utilizes a computer to design and revise items. When you have a final design, you enter it as a program and send it to a computer-aided manufacturing system. CAM systems are systems that consist of all facets of process preparation, production planning, scheduling, machining, and quality assurance.
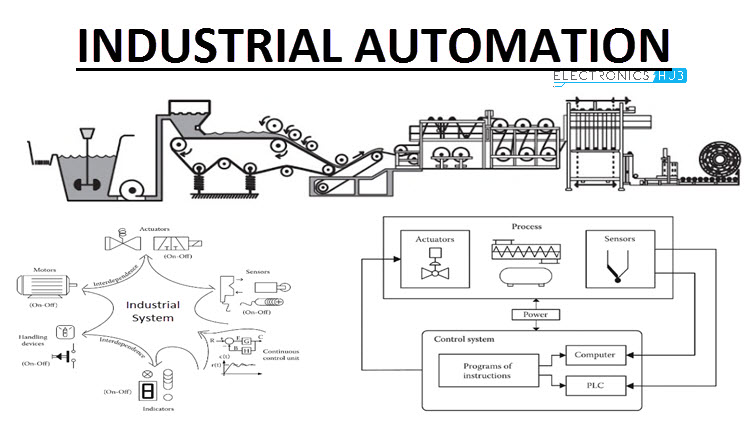
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Computer system mathematical control is feasible due to PLCs, which are solidified microprocessors that integrate and integrate signals from sensing units with instruction actuators. Human-machine interfaces act as a front for PLCs, giving a user-accessible means to program and control procedures and jobs.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC)
Utilizing a computer system cpu jointly with numerical control permits you to store, edit, and review coded part programs, if errors emerge. You can create part programs by starting at the command line or by “teaching” a machine to perform steps that the system then files in code. These steps are called part program commands.
Trends in Production Automation
The social memes for automation, symbolized by movies like Metropolis and Modern Times, illustrate megalithic, uncaring, and hurtful manufacturing ventures, with people playing the duties of gears.
However, it’s possible that in the future, automation will provide people with more safety, more independence, and more options. In the “gig economic climate,” automation and digitization may supply chances for increased specialist autonomy, where individuals utilize their liberty to choose where they live and just how they operate.
Additional proof that automation produces choices may be that manufacturing in the future will focus less on mass production and more on customization. These unique products might come from micro factories, smaller establishments that can not only give local employment opportunities and recycling benefits, yet additionally produce little consumer goods as needed, potentially requiring fewer delivery resources.

